Social health is defined as how a person evaluates his or her performance against social. So the issue of health and well-being is socially structured. Social health is affected by many factors. In this study, students' social health has been researched under the influence of the effective factor of family social capital. This research is a descriptive and survey research in terms of applied purpose and in terms of data collection. The statistical population of the study consists of students of public schools in Shahroud, which is equal to 6200 people, and according to Cochran's formula, 291 people were selected to collect research data. According to random sampling, three schools (Ikhlas, Moallem and Motahhari) were selected from public schools to collect information. The theoretical foundations selected and used in this study were combined. Keyes and Shapiro theories were used for the dependent variable of the research and theories were used to analyze the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable: Keys, Reef, Larsen, Block & Breslow, Francis Fukuyama, Robert Putnam, James Coleman, Pierre Bourdieu, Marx and Durkheim. The results showed that all three components of social capital (family social trust) had a positive and strong relationship with Pearson coefficient: 0.61 and (family social cohesion with relationship coefficient: 0.54 and family social participation with relationship coefficient: 0.47) with dependent variable (Social health of Shahroud students) has had a positive and direct impact on the average. Family social trust in the first place and family social cohesion in the second degree were able to explain 39% of the variance of the dependent variable.
| Published in | Social Sciences (Volume 13, Issue 6) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.ss.20241306.18 |
| Page(s) | 309-320 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Science Publishing Group |
Family Social Capital, Social Trust, Social Cohesion, Social Participation and Students' Social Health
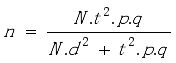
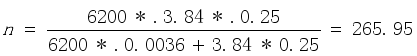
Variables | Number of Item | Reliability |
|---|---|---|
Family Social trust | 7 | 0.90 |
Social cohesion of the family | 5 | 0.88 |
Social participation of the family | 6 | 0.83 |
Social capital | 18 | 0.94 |
Social prosperity | 4 | 0.79 |
Social Solidarity | 3 | 0.76 |
Social solidarity | 3 | 0.91 |
Social acceptance | 5 | 0.81 |
Social participation | 5 | 0.84 |
Social health | 20 | 0.91 |
variables | Family social health variable | Family social capital variable | Students' father's education | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
High | Moderate | Low | High | Moderate | Low | Master's degree and higher | Master's degree and bachelor's degree | Diploma and below | |
Groups | 106 | 161 | 24 | 180 | 88 | 23 | 27 | 92 | 172 |
Frequency | 36.4 | 55.3 | 8.2 | 61.9 | 30.2 | 7.9 | 9 | 32 | 59 |
Percent | |||||||||
Variable | R | R2 | Standard error | T-Value | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The social capital of Shahrood students' families | 0.62 | 0.38 | 0.040 | 13.382 | 0.000 |
Variable | R | R2 | Standard error | T-Value | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Social trust of Shahrood students' families | 0.60 | 0.36 | 0.092 | 12.952 | 0.000 |
Variable | R | R2 | Standard error | T-Value | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Social cohesion of Shahrood students' families | 0.54 | 0.29 | 0.112 | 10.780 | 0.000 |
Variable | R | R2 | Standard error | T-Value | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Social participation of Shahrood students' families | 0.47 | 0.22 | 0.146 | 9.126 | 0.000 |
Variables | Non-standard coefficients | Beta Coefficient | T Coefficient | Sig | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
B | Std. Error | |||||
constant | 31.229 | 2.613 | 11.953 | 0.000 | ||
1 | Social trust of Shahrood students' families | 0.887 | 0.123 | 0.450 | 7.192 | 0.000 |
2 | Social cohesion of Shahrood students' families | 0.517 | 0.141 | 0.229 | 3.658 | 0.000 |
The dependent variable | The three independent components of research | R | R2 | SEE (Standard error) | R2 Adjusted | F Test amount (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Social health of Shahrood students | 1. Social trust of students' families 2. Social cohesion of students' families 3. Social participation of students' families | 0.629 | 0.395 | 10.457 | 0.391 | 94.166 (0.000) |
Social trust of students' families | 1. Social cohesion of students' families 2. Social participation of students' families | 0.760 | 0.577 | 4.436 | 0.574 | 196.514 (0.000) |
Social cohesion of students' families | 1. Social trust of students' families 2. Social participation of students' families | 0.712 | 0.507 | 4.179 | 0.504 | 148.189 (0.000) |
Components | Direct effect (without intermediary) | Indirect impact (mediated) | The effect of the total components |
|---|---|---|---|
Social trust of students' families | 0.45 | 0.49 * 0.45= 0.22 | 0.67 |
Social cohesion of students' families | 0.23 | 0.42 * 0.23= 0.10 | 0.33 |
Social participation of students' families | --------- | 0.43 * 0.67= 0.29 0.29 * 0.33= 0.10 | 0.39 |
WHO | World Health Organization |
PNU | Payam NOOR University |
TMU | Tarbiat Modares University |
| [1] | Alikhan Gorgani, Ruhollah; and Moradi, Hossein. (2013). an introduction to social capital (concepts and applications). Tehran" Azarakhsh Publications. [Persian] |
| [2] | Alini, Mohammad. (2012). Social capital in Islamic teachings. Qom: Bostan Ketab, Qom Publishing House. [Persian] |
| [3] | Alipour, Mahdis. (2011). the role of television health and medical programs on the physical and mental health of messengers. Master's thesis, Allameh Tabatabei University, Tehran. [Persian] |
| [4] | Bokharaei, Ahmad; Sharbatian, Mohammad Hassan; Imani, Nafiseh. (2015). Sociological study of women's social health and factors influencing it (case study: Women of District 4 of Tehran). Contemporary Sociology Research Quarterly, 4(7), 29-54. [Persian] |
| [5] | Carrillo Alvarez, Elena, Kawachi, Ichiro, and Riera Romani, Jordi (2016), "Family social capital and health – a systematic review and redirection", Sociology of Health & Illness, Vol. xx No. xx 2016 ISSN 0141-9889, pp. 1–25. |
| [6] | Devas, D. A. (2015), "Survey in social research", translated by Hoshang Nayebi, Tehran, Ney publication. [Persian] |
| [7] | Fukuyama, Francis; Portes, Alejandro; Efe, Klaus; Pantham, Robert; Coleman, James Samuel; Bourdieu, Pierre; Woolcock, Michael. (2010). Social Capital: Trust, Democracy and Development. Hasan Pouyan and Afshin Khakbaz. Tehran: Shirazeh Publications. [Persian] |
| [8] | Ghiyasi, Mojtaba, Sarlak, Ahmad, Ghaffari, Hadi. (2020). Investigating the relationship between social capital, health capital and economic growth in the provinces of the country. Scientific quarterly of applied economic theories. 7(3), 131-156 [Persian]. |
| [9] | Ghorbani, Sara; Jahanizadeh, Mohammadreza; Mirbod, Seyed Mehran; Omidi, Leila. (2020). Examining the relationship between psychological and social capitals and social health according to the mediating variable of social support. Social Psychology Research Quarterly, 10(38), 83-100. [Persian] |
| [10] | Greene, T., Gross, R., Amsel, L., & Hoven, C. W. (2018). The mental health of children and adolescents exposed to 9/11: Lessons learned and still to be learned. World Trade Center Pulmonary Diseases and Multi-Organ System Manifestations, 5, 121-136. |
| [11] | Hashemipour, Maryam, Farahaninia, Marhamat, Kashaninia, Zahra and Haghani, Hamid (2020)," Relationship between Social Capital and Health-promoting Lifestyle in Nursing Students", Journal of Client-Centered Nursing Care, 6(4), pp. 223-230. |
| [12] | Hemati Rad, Farzaneh; Keshavarz, Amrollah; Momeni, Hassan. (2018). the relationship between social capital and social health in secondary school students. Social Work Quarterly, 7(2), 7-14. [Persian] |
| [13] | Heydarabadi, Abolghasem; Matlabi, Manijhe; Rahmani Firouzjah, Ali; Abbasi Esfajir, Ali Asghar. (2020) in a sociological study of the relationship between social capital and social health (a case study of students in 5 district of Tehran). Journal of Sociological Studies, 13(47), 59-70. [Persian] |
| [14] | Islam Dost, Behnam. (2020). Investigating the relationship between social capital and social health among citizens over 20 years old in Urmia city. Scientific Journal of Police Science, Applied Research Office of West Azarbaijan Province, 11(46), 47-70. [Persian] |
| [15] | Ji, Ying, Yun, Qingping, Jiang, Xuewen and Chang Chun (2020), " Family SES, family social capital, and general health in Chinese adults: exploring their relationships and the gender-based differences", BMC Public Health, |
| [16] | Keyes, C. M. (1998). Social well-being. Social psychology Quarterly, 61(2), 121-140. |
| [17] | McPherson, Kerri E, Kerr, Susan, McGee, Elizabeth, Morgan, Antony, Cheater, Francine M, McLean, Jennifer and Egan, James (2014)," The association between social capital and mental health and behavioural problems in children and adolescents: an integrative systematic review", BMC Psychology, PP 2-16. |
| [18] | Morovati, Nasrin; Fathi, Mansour and Morovati, Nader (2017). The relationship between the level of economic-social base and the social health of the youth of Ghorve city. Strategic Studies of Sports and Adolescents, 38, 169-184. [Persian] |
| [19] | Moshkboy, Shirin. (2017). Investigating the social factors affecting the social health of young couples in Gheshm city. Master's thesis, Islamic Azad University, Bandar Abbas branch. [Persian] |
| [20] | Nazoktabar Hossein, Babaei Ensieh, Saffarfar Amir (2019), "Investigating the relationship between Islamic lifestyle and social health and mental security of students", Islamic lifestyle with a focus on health, 3(3), 32-40. [Persian] |
| [21] | Omidian, Mehdi, Esmaeilpour Ashkaftaki, Mahmoud (2020), "Prediction of social support of students based on the components of social capital and psychological capital in the crisis of the Corona epidemic", Social Psychology Research, No. 3 ¬and ¬9, fall 99, pp. 179-163. [Persian] |
| [22] | Piran Gheidari, Mohammad Hassan; Farzaneh, Saiffollah; Hyderabadi, Abolghasem; Gholipour, Majdeh. (2020). the role of cultural capital in social health: a case study of citizens of 22 districts of Tehran. Paish, 20(1), 7-14. [Persian] |
| [23] | Putnam, R. D. (2011). Bowling alone: The collapse and revival of American community. Simon and Schuster. |
| [24] | Radan, Fatima. (2019). Prediction of social vitality based on social capital of female students. Social Capital Management, 6(3), 219-236. [Persian] |
| [25] | Sabatino, M. (2019). Economic resilience and social capital of the Italian regions. International Review of Economics and Finance, |
| [26] | Saffari, Mohsen; and Shojaeizadeh, Davood. (2008). Health education and health promotion. Tehran: Samit Publications. |
| [27] | Seyed Kalan, Seyed Mohammad; Maleki Avarsin, Sadegh. (2020). Explaining the concept of social health based on the perspective of the Holy Quran (focusing on Surah Kahf). Islam and Health Journal, 5(1), 45-54. [Persian] |
| [28] | Solhi, Mahnaz, Yousefi Labani, Javad, Khosravi, Bahar, Fatahi and Rustaghi, Siddiqa (2018). The relationship between background variables and social capital in Iranian medical students. Scientific-Research Journal of Sabzevar University of Medical Sciences, Volume 27, Number 1, April and May 1999, pp. 113-120. [Persian] |
| [29] | Wu, Cary (2021), " Social capital and COVID-19: a multidimensional and multilevel approach", CHINESE SOCIOLOGICAL REVIEW, 2021, VOL. 53, NO. 1, 27–54. |
| [30] | Wyatt, T. J., Oswalt, S. B., & Ochoa, Y. (2017). Mental health and academic performance of first-year college students. International Journal of Higher Education, 6(3), 178-187. |
| [31] | Zarei Mateen, Hassan; Mohammadian, Behzad. (2016). Social capital management. Tehran: Mehraban Kitab Publications. |
APA Style
Jelodar, S. M., Khorsandi, J., khani, A., Samiei, M., Jamali, M. (2024). A Study of Social Capital on the Social Health of Students (Field Survey of First Secondary Schools in Shahrood City). Social Sciences, 13(6), 309-320. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ss.20241306.18
ACS Style
Jelodar, S. M.; Khorsandi, J.; khani, A.; Samiei, M.; Jamali, M. A Study of Social Capital on the Social Health of Students (Field Survey of First Secondary Schools in Shahrood City). Soc. Sci. 2024, 13(6), 309-320. doi: 10.11648/j.ss.20241306.18
AMA Style
Jelodar SM, Khorsandi J, khani A, Samiei M, Jamali M. A Study of Social Capital on the Social Health of Students (Field Survey of First Secondary Schools in Shahrood City). Soc Sci. 2024;13(6):309-320. doi: 10.11648/j.ss.20241306.18
@article{10.11648/j.ss.20241306.18,
author = {Shahram Mollania Jelodar and Jafar Khorsandi and Alireza khani and Mostafa Samiei and Maryam Jamali},
title = {A Study of Social Capital on the Social Health of Students (Field Survey of First Secondary Schools in Shahrood City)
},
journal = {Social Sciences},
volume = {13},
number = {6},
pages = {309-320},
doi = {10.11648/j.ss.20241306.18},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ss.20241306.18},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.ss.20241306.18},
abstract = {Social health is defined as how a person evaluates his or her performance against social. So the issue of health and well-being is socially structured. Social health is affected by many factors. In this study, students' social health has been researched under the influence of the effective factor of family social capital. This research is a descriptive and survey research in terms of applied purpose and in terms of data collection. The statistical population of the study consists of students of public schools in Shahroud, which is equal to 6200 people, and according to Cochran's formula, 291 people were selected to collect research data. According to random sampling, three schools (Ikhlas, Moallem and Motahhari) were selected from public schools to collect information. The theoretical foundations selected and used in this study were combined. Keyes and Shapiro theories were used for the dependent variable of the research and theories were used to analyze the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable: Keys, Reef, Larsen, Block & Breslow, Francis Fukuyama, Robert Putnam, James Coleman, Pierre Bourdieu, Marx and Durkheim. The results showed that all three components of social capital (family social trust) had a positive and strong relationship with Pearson coefficient: 0.61 and (family social cohesion with relationship coefficient: 0.54 and family social participation with relationship coefficient: 0.47) with dependent variable (Social health of Shahroud students) has had a positive and direct impact on the average. Family social trust in the first place and family social cohesion in the second degree were able to explain 39% of the variance of the dependent variable.
},
year = {2024}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - A Study of Social Capital on the Social Health of Students (Field Survey of First Secondary Schools in Shahrood City) AU - Shahram Mollania Jelodar AU - Jafar Khorsandi AU - Alireza khani AU - Mostafa Samiei AU - Maryam Jamali Y1 - 2024/12/30 PY - 2024 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ss.20241306.18 DO - 10.11648/j.ss.20241306.18 T2 - Social Sciences JF - Social Sciences JO - Social Sciences SP - 309 EP - 320 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2326-988X UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ss.20241306.18 AB - Social health is defined as how a person evaluates his or her performance against social. So the issue of health and well-being is socially structured. Social health is affected by many factors. In this study, students' social health has been researched under the influence of the effective factor of family social capital. This research is a descriptive and survey research in terms of applied purpose and in terms of data collection. The statistical population of the study consists of students of public schools in Shahroud, which is equal to 6200 people, and according to Cochran's formula, 291 people were selected to collect research data. According to random sampling, three schools (Ikhlas, Moallem and Motahhari) were selected from public schools to collect information. The theoretical foundations selected and used in this study were combined. Keyes and Shapiro theories were used for the dependent variable of the research and theories were used to analyze the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable: Keys, Reef, Larsen, Block & Breslow, Francis Fukuyama, Robert Putnam, James Coleman, Pierre Bourdieu, Marx and Durkheim. The results showed that all three components of social capital (family social trust) had a positive and strong relationship with Pearson coefficient: 0.61 and (family social cohesion with relationship coefficient: 0.54 and family social participation with relationship coefficient: 0.47) with dependent variable (Social health of Shahroud students) has had a positive and direct impact on the average. Family social trust in the first place and family social cohesion in the second degree were able to explain 39% of the variance of the dependent variable. VL - 13 IS - 6 ER -